Why integrate CSR into your corporate policy?
Key points of the article
Over the past few years, ecological awareness has become increasingly widespread in our society.
Adopting a responsible lifestyle, taking initiatives to preserve the environment, promoting the local economy – we can’t count the number of little habits encouraged on a daily basis.
How can we translate these changes into business?
More and more organizations are looking at ways of integrating a CSR approach into their business activities.
Indeed, the principle of Corporate Social Responsibility is becoming increasingly important.
CSR embodies the contribution of organizations to sustainable development, which includes not only environmental, but also social and governance aspects.
Our article reveals all the important information you need to know about CSR.
Become a true expert on the CSR approach to business!
What you need to know about Corporate Social Responsibility
Defining CSR and its objectives
CSR stands for Corporate Social Responsibility.
The Confederation defines this principle as follows: “CSR deals with the effects of corporate activities on society and the environment”.
In other words, companies have a duty to adjust their activities in such a way as to limit negative impacts through a responsible approach.
In this way, a CSR company contributes not only to protecting the environment, but also to improving living conditions in society and promoting a healthy, fair business economy.
A successful CSR approach must therefore have a positive impact on 3 distinct pillars.
These are the CSR pillars:
The social pillar
This sector covers all issues relating to human beings and their life in society.
It covers a wide range of issues relating to health, education, living and working conditions.
It involves thinking about measures that can guarantee the well-being and rights of everyone.
In this way, the social pillar of CSR covers issues such as well-being in the workplace, equal pay and respect for diversity…
The environmental pillar
This section focuses on issues relating to greenhouse gas emissions, waste and environmental pollution.
This pillar highlights recycling, renewable energy consumption and all other measures aimed at reducing the environmental impact of the structure concerned.
In a company, the environmental pillar covers issues such as transport, waste management, energy use, etc.
The economic pillar
This is the economic system adopted by a structure.
It includes issues related to purchasing policy, suppliers and manufacturing processes.
A company committed to a CSR approach will focus its actions on adopting a less resource-intensive mode of production, promoting the local economy and implementing a responsible purchasing policy.
Other actions are also possible, depending on the company and its activities.
To conclude, CSR is, above all, an approach to corporate investment in sustainable development.
It involves actions designed to protect the environment, but also to guarantee a quality working environment for employees and external relations in line with this commitment.
CSR and the ISO 26000 standard
This has given you an insight into the fundamentals of CSR.
Next, we’ll take a closer look at the rules governing the concept of CSR.
This will enable us to understand the framework established to guide the actions to be taken.
The ISO 26000 standard is the international benchmark for CSR.
It was developed in 2010 by over 90 countries, and is coordinated by the ISO organization.
This standard defines the framework for developing a CSR strategy within a company, serving as a guide and laying down the fundamental principles of CSR.
It is valid for all types of organization.
It is used by national standards to measure and assess the extent to which companies are committed to sustainable development.
The ISO 26000 standard defines CSR in terms of :
- Contribute to sustainable development and the betterment of society
- Taking stakeholders into account
- Respect for the law
- Adopt responsible behavior that is reflected throughout the organization and its relationships.
The ISO 26000 standard also sets out the basic principles of CSR.
These principles are supplemented by 7 central questions designed to guide the actions to be implemented.
The standard is thus based on the following 7 principles:
Corporate accountability: the organization must be accountable for its activities and their impact on the 3 pillars mentioned above.
It also means accepting to be evaluated and ensuring the legality of all steps taken.
Transparency: this principle is linked to the structure’s communication on the reality of its CSR policy actions.
It also means making clear, proven information available.
Ethics: this means developing our actions in a spirit of integrity and equality.
Respect for stakeholders: this means clearly identifying the company’s stakeholders and respecting their needs.
Legality: the company has a duty to comply with the law, and to take account of possible changes.
Its approach must always be in line with established standards.
Compliance with international standards: the company must also comply with international standards.
In the event of France’s legal silence on certain concepts, these standards are authoritative.
Respect for human rights: companies must offer activities and a working environment that respect human rights.
These principles form the basis of the ISO 26000 standard, and thus define the guiding principles of any CSR strategy.
A company embarking on a new Corporate Social Responsibility policy must ensure that it is fully consistent with these pillars.
Note that certain rules are already mandatory.
Failure to comply could result in severe penalties.
Why integrate CSR into your business?
Incorporating a CSR approach into your business is a complex undertaking, but one that is full of advantages and benefits.
Indeed, a company that distinguishes itself as actively committed to Corporate Social Responsibility benefits from an attractive image on the market.
With CSR at the heart of our society’s challenges, the company’s inspiring image is sure to attract attention.
Incorporating CSR into your brand image can be a real competitive advantage.
CSR also creates a positive image internally.
Indeed, all employees can be involved in the project, thus creating genuine team cohesion.
In fact, we recommend that you make internal communications a central part of your CSR action plan.
In this way, employees can be proud to work for a human and committed organization.
Productivity is bound to improve!
It’s also a good way of communicating with the outside world.
A company recognized as being committed to CSR will also be more attractive to potential recruitment candidates.
Finally, adopting a CSR approach can also change production processes and generate savings!
How do you set up a CSR strategy?
Diagnosis
The first step is to carry out a diagnosis.
This involves taking stock of the company and assessing its level of maturity in relation to the CSR pillars.
The company will use data such as the employee satisfaction index, the ethics of the methods used, etc. This reflection will help determine the guidelines of the future CSR strategy and prioritize its challenges.
It is also an opportunity to define the project’s stakeholders.
The aim is to establish their needs and interests, so that these can be taken into account throughout the development of the strategy.
Above all, the diagnosis acts as a working basis.
It is a co-construction tool whose aim is to propose a methodology for the future CSR action plan.
Define the action plan
The action plan is defined after the CSR diagnosis.
It is designed to respond to the company’s raison d’être and deploy the chosen CSR policy.
It is structured around the 7 major questions defined by the ISO 26 000 standard:
- Governance: this covers all issues relating to the company’s management and hierarchical organization.
- Human rights: these are issues linked to people and their daily development within the company.
- Working conditions: guaranteeing working conditions that respect rights, codifying relations between different statuses (employees/supervisors, for example).
- Loyalty in our practices: ensuring an honest approach in line with the principle of ethics.
- Consumer protection issues: actions to ensure transparency and respect for the consumer.
- Promoting local development: this refers to actions that will enhance the local economy.
- Protecting the environment: from reducing pollution to saving energy and protecting biodiversity.
The above questions thus serve as a framework for a company’s CSR policy.
The action plan will then be defined as a response to the major questions through concrete actions.
These actions will be in line with the course of action adopted by the company during the diagnostic phase.
This is followed by the deployment phase, when the actions are implemented throughout the company.
The key to successful deployment lies in communication, both internal and external.
The company needs to communicate as much as possible with all its employees to ensure optimum internal integration.
It must also dialogue with its external partners to ensure a strong impact on the public.
Possible actions to be taken
Here are a few examples of actions you can take as part of your CSR roll-out, covering the various pillars.
Actions relating to the social pillar :
- Offer suitable premises (space, equipment, etc.)
- Comply with health and safety standards
- Sports and team-building activities
- Promoting diversity
Actions relating to the environmental pillar :
- Draw up a waste reduction plan
- Favoring renewable energies
- Reduce CO2 emissions (carpooling, telecommuting)
- Recycling
Actions relating to the economic pillar :
- Promoting local partners
- Drawing up an Ethics Charter
- Promoting short circuits
- Enhancing employment opportunities for young people and seniors
What are the CSR indicators?
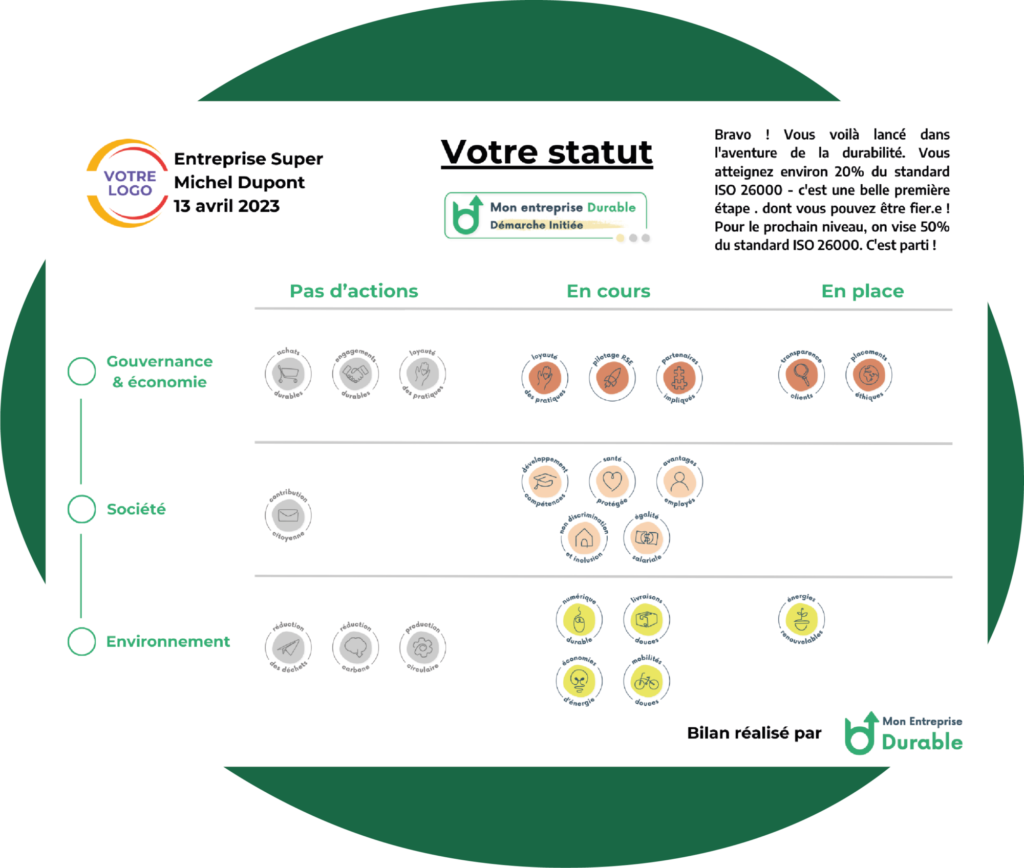
Once your CSR actions have been implemented, the key is to carefully monitor their impact.
The final step is to evaluate your CSR policy.
CSR labels and reporting
There are many CSR tools available to help you in your approach and measure its effectiveness, including reporting and labels.
Reporting is a clear and precise assessment of the impact of a company’s activities from an economic, environmental, social and societal point of view.
Fully in line with the principles of transparency and accountability, it enables companies to evaluate themselves.
It also attests to the credibility of their commitment in the eyes of customers and partners.
Reporting acts as a showcase, but also as proof of the company’s investment.
It must establish a clear and rigorous follow-up.
The following labels are competent to assess a company’s CSR strategy.
If the company meets the criteria, it will be rewarded with a label that guarantees its credibility.
These include :
Eco Entreprise : This Swiss certification assesses a company’s overall performance based on ISO 26000 standards. The assessment is based on an audit carried out by an external certifier. It enables better evaluation when awarding public contracts. The certified company can wear its logo for 3 years.
B-Corp: created in 2006 in the United States, this label has been present in Switzerland since 2019. Its role is to assess a company’s overall performance, based on its responses to the online reference system and the documents provided. Labeled companies are reassessed every 3 years.
CSR is an increasingly important concept in the development of a company’s activities. In addition to enhancing its image, it conveys a message with strong values! We hope we’ve been able to clarify your vision of CSR in business!